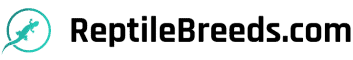The process of sexing leopard geckos means that you’re identifying their gender based on distinct physical characteristics. This might sound technical, but in essence, it’s about telling male and female geckos apart. Why? Because knowing their gender is crucial. For pet owners, breeders, and reptile enthusiasts, gender identification not only informs care routines but is vital for breeding plans. Imagine naming your gecko Lucy only to find out it’s a Louie!
Age Matters: You can best determine the gender of a leopard gecko after it’s around 6 months old.
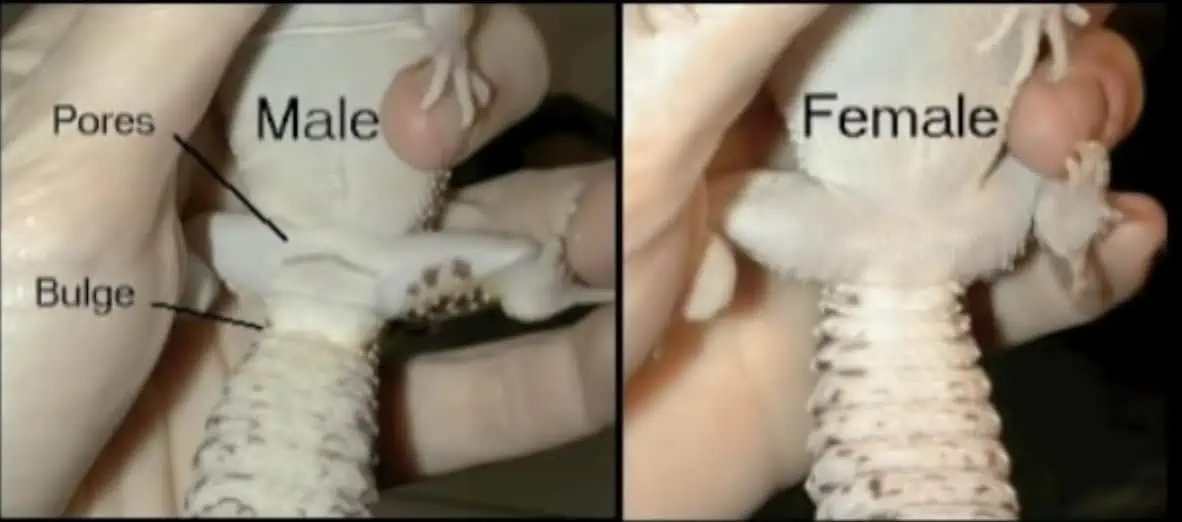
Physical Differences: Male leopard geckos usually have broader heads, a noticeable hemipenal bulge, and distinct preanal pores. Females lack the pronounced bulge and have fainter pores.
Safe Handling: When inspecting the gecko, ensure you pick it up safely, supporting its head, neck, and hind legs. Never grab the tail.
Optimal Environment: Always conduct the examination in a well-lit area on a soft surface to minimize stress.
Aftercare: Return the gecko to its tank gently, ensuring a stress-free environment for it to relax.
Sexing Leopard Geckos: How To
Sexing leopard geckos is a pivotal practice that goes beyond mere curiosity. Correctly identifying a gecko’s gender plays a significant role in ensuring its proper care and setting the stage for effective breeding. Whether you’re a pet owner or a budding reptile breeder, understanding the gender of your leopard gecko is paramount.
Gender identification is based on a series of distinct physical features. It’s not just about giving a quick glance; instead, it involves careful observation of multiple characteristics that differentiate a male from a female gecko. For example, the presence or absence of a hemipenal bulge, the size and shape of their heads, and the visibility of preanal pores can all give away a gecko’s gender.
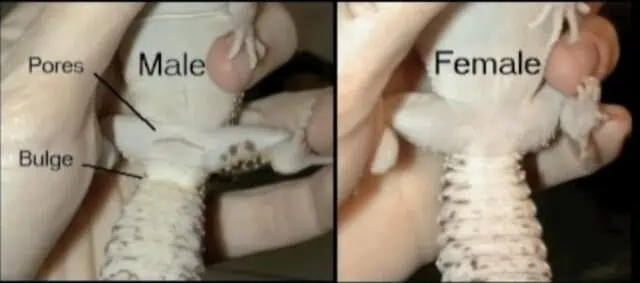
So, how does one go about sexing leopard geckos? It’s about getting a good look at them, preferably in a well-lit area, and checking for the telltale signs. While there’s a bit of a learning curve, with time and experience, distinguishing between male and female geckos becomes second nature.
When Can You Accurately Determine the Sex of a Leopard Gecko?
Determining the sex of a leopard gecko is crucial. But timing is key. Too early, and the signs aren’t clear. So, when is the right time? Most experienced breeders and reptile experts agree on a timeline.
A leopard gecko is ready for sex determination around the 6-month mark. Before this age, the physical features distinguishing males from females aren’t fully developed. By waiting until they’re about 6 months old, you increase your chances of accuracy. So, patience is vital. Trust in the knowledge of those who’ve been in the reptile game for a while.
Step by Step – How To Tell Female and Male Leopard Geckos Apart
Telling male and female leopard geckos apart can be a bit tricky, especially for beginners. But with a systematic approach and keen observation, it becomes straightforward.
Pick The Right Spot To Do It
Picking the right spot to determine the gender of your leopard gecko is more critical than it might initially seem. The location can significantly affect the accuracy of your observation and the safety of your gecko. A well-lit area is essential. Why? Because you’ll need to observe subtle physical differences that might be easily missed in dim light.
But it’s not just about lighting. The surface on which you place the gecko matters too. A soft surface is the best choice. It offers two main benefits: it ensures the gecko’s comfort and minimizes the risk of injury. Remember, these creatures can be delicate.
Now, you might wonder why not just use a low-lit area with a flashlight or another light source? Low light conditions can be misleading. Shadows and poor angles can distort what you see, leading to incorrect gender identification. Plus, working in such conditions can stress out your gecko, potentially leading to behavioral issues or health concerns.
Do Your Research Beforehand
Diving into the world of leopard geckos without adequate research can be likened to navigating a maze blindfolded.
Particularly when it comes to gender identification, understanding the physical differences between male and female leopard geckos is paramount. Not only does this knowledge ensure accurate pairing and breeding, but it also helps avoid potential conflicts between geckos.
So, where should you start? In today’s digital age, a quick online search can yield a wealth of information. However, it’s always a good idea to have a visual reference handy. Having your computer or phone opened to a clear image illustrating the physical differences can serve as a useful guide.
This visual aid can help you compare and contrast what you’re seeing in real-time, minimizing the chances of making an error.
Pick Up the Gecko
Handling a leopard gecko, especially for the purpose of sexing, requires a combination of gentleness and precision. It’s essential to pick up the gecko in a way that ensures its safety and comfort.
Begin by placing your thumb and index finger gently around its head and neck area. This provides stability and control while ensuring that the gecko doesn’t feel threatened or overly restrained.
While you’re securing the head and neck, it’s crucial to hold the gecko firmly but gently. Rough handling can cause stress or injury. It’s also worth noting that one should always avoid grabbing the gecko by its tail.
Leopard geckos have a defense mechanism where they can drop their tails if threatened, so it’s essential to be cautious.
Your other hand plays an equally vital role. Use it to support the gecko’s hind legs. This secondary support helps in balancing the gecko and ensuring it doesn’t wriggle out of your grip. Once you have a firm but gentle hold, lift the gecko at a slight angle, which allows you to easily view the vent for gender identification.
It’s tempting for some to turn the gecko upside-down for a clearer view. However, unless you’re experienced, it’s best to avoid this method as it can be stressful for the gecko.
Look for the Differences Between Male and Female Leopard Geckos
Determining the sex of a leopard gecko requires keen observation of their physical differences. Male and female leopard geckos exhibit distinct traits that can help you accurately identify their gender.
Firstly, males typically have a broader head and a thicker neck compared to females.
The base of the tail is also generally larger in males due to the presence of hemipenal bulges, which females lack.
Hemipenal bulges are two noticeable raised areas on the underside of the tail, right before the vent. These bulges are indicative of the male’s reproductive anatomy.
Females, on the other hand, have a slimmer appearance without any pronounced hemipenal bulges.
Another distinct characteristic in females is the absence of prominent preanal pores. While both genders have preanal pores, they are more defined and visible in males, often appearing as a V-shaped line of pores in front of the vent.
Place The Gecko Back In Its Tank, Carefully
After determining the sex of the leopard gecko, the next step is to place the gecko back in its tank. This step is as crucial as picking it up because it ensures the gecko’s well-being and comfort.
Ensuring a stress-free environment is essential for the gecko’s overall health. After handling, the gecko might feel agitated or stressed. By providing a serene and familiar setting, you allow the gecko to relax and return to its normal behavior.
When returning the gecko to its tank, use gentle and deliberate movements. Hold the gecko similarly to how you picked it up, supporting its head, neck, and hind legs. Lower the gecko close to the ground of the tank before releasing, ensuring you don’t drop it from a height. Always avoid rushing the process and handle the creature with utmost care to ensure it is safely placed back.
Gender Identification: Physical Differences Between Males and Females
Identifying the gender of a leopard gecko is pivotal for many reasons, from pairing for breeding to providing specialized care. Understanding the physical differences between male and female geckos allows owners and breeders to make informed decisions tailored to each individual gecko’s needs.
Broader Heads
One defining physical characteristic of male leopard geckos is the presence of a broader head. As they grow and reach sexual maturity, males typically develop larger and more pronounced heads compared to females. This difference becomes especially noticeable when comparing mature individuals side by side.
Hemipenal Bulge
The hemipenal bulge stands out as a prominent physical trait that distinguishes a male leopard gecko from its female counterpart. Positioned right beneath the vent at the tail’s base, this bulge becomes pronounced in male geckos as they approach sexual maturity.
Notably, female geckos lack this characteristic, making it an essential feature to observe when identifying gender.
Preanal Pores
The preanal pores present another distinguishing feature between male and female leopard geckos. Both genders possess these pores, but there’s a noticeable difference in their visibility.
In male geckos, these pores are easily discernible and often excrete a waxy substance laden with pheromones. This secretion plays a crucial role, allowing males to mark their territory and court potential mates.
On the other hand, female geckos have these pores too, but they appear faded and are almost imperceptible.
Cloacal Spurs
Cloacal Spurs are another distinguishing feature between male and female leopard geckos.
Located on the vent area of the gecko, these are small, pointy scales that are readily apparent in males. Males utilize these spurs during mating.
Contrastingly, females do not possess these spurs, making their absence a clear gender identifier.
Hind Legs
The hind legs of a leopard gecko provide subtle clues to their gender. Typically, male leopard geckos boast hind legs that are thicker and more muscular in appearance.
This robustness contrasts with the more slender and delicate hind legs seen in females.