Leopard Geckos, known scientifically as Eublepharis macularius, are among the most popular reptilian pets across the globe. With their distinct mottled patterns, engaging personalities, and relatively easy care requirements, it’s no wonder they’ve won the hearts of reptile enthusiasts and novices alike.
But beyond their captivating appearance lies a fascinating tale of evolution and adaptation, honed over millions of years to suit their native desert environments.
For potential and current leopard gecko owners, diving deep into these adaptations isn’t just a journey of curiosity—it’s a path to understanding their pet better and providing a care regimen that aligns with their intrinsic nature.
Evolutionary History of Leopard Geckos
From the vast, sandy stretches of Asian deserts to the cozy corners of our homes, the journey of the Leopard Gecko is nothing short of fascinating. These resilient creatures, over eons, have navigated a world constantly in flux, evolving and adapting to ensure their survival. As we trace their evolutionary footsteps, we gain insights not just into their biology, but also their rise to popularity in the world of herpetology. Their transformations, both subtle and significant, reveal a narrative of survival, adaptation, and eventual domestication. Whether it’s their unmistakable skin patterns, nocturnal habits, or their intriguing behaviors, every facet of the Leopard Gecko is a testament to millions of years of evolutionary artistry.
Origins and Ancestry
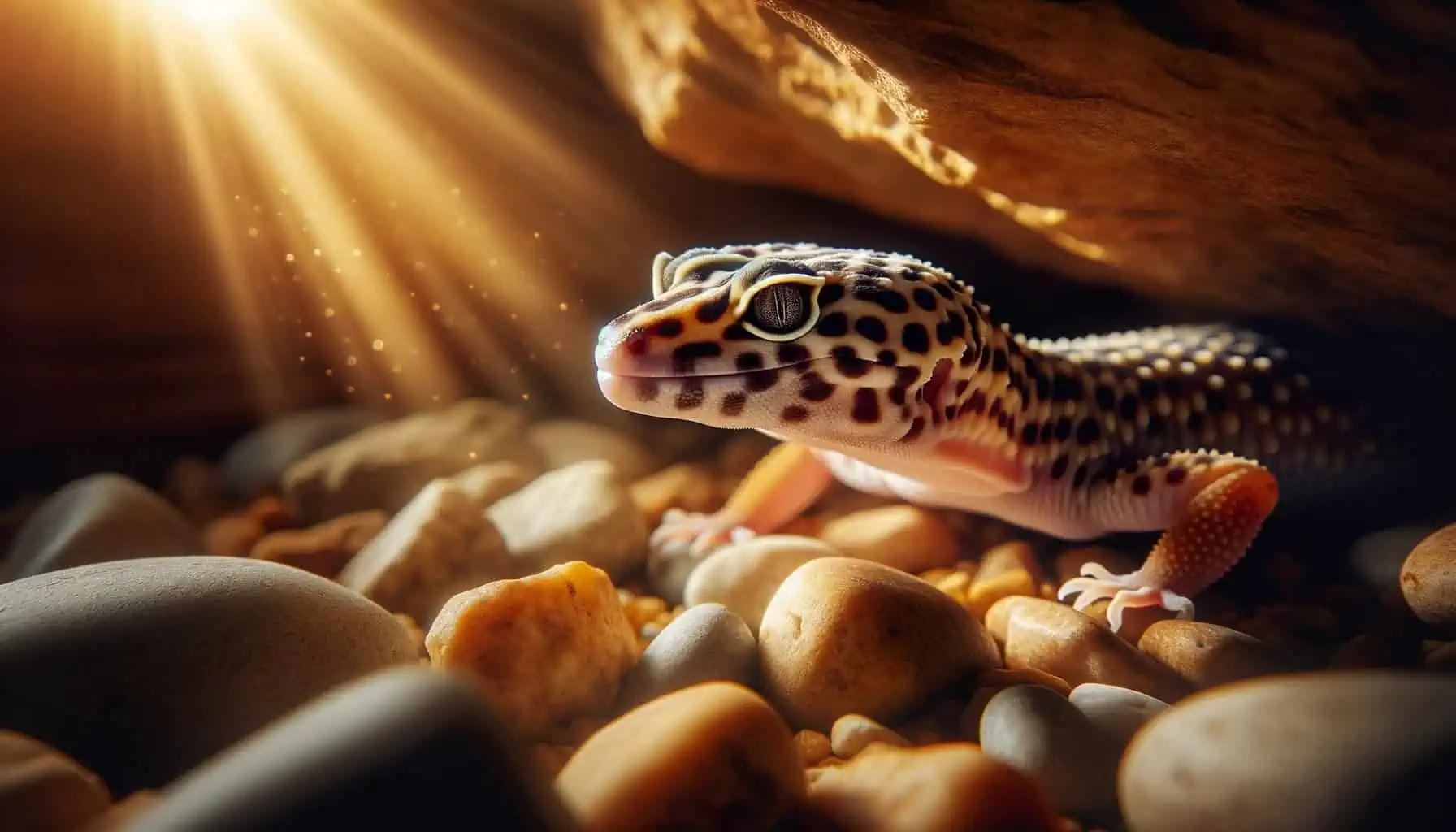
The majestic tapestry of the Leopard Gecko’s lineage stretches back to the vast Asian desert regions, a testament to their incredible endurance and adaptability. Officially known as Eublepharis macularius, these reptiles have carved their niche in some of the most unforgiving terrains on our planet.
Diving into the depths of the leopard gecko ancestry reveals that they’re a part of an ancient group of ground-dwelling geckos. Unlike many of their arboreal cousins who dwell in trees, these desert reptiles have evolved specific features to thrive in arid, sandy environments. Their robust build and mottled skin patterns, for instance, are direct outcomes of their ancestry and the demands of their native habitat.
Their closest relatives in the wild can be found scattered across the desert landscapes of Asia, each with its unique set of adaptations, yet sharing a common lineage that echoes the tales of ancient reptilian families.
Transition to Domestication
The journey from wild, sandy terrains to the cozy confines of terrariums wasn’t a brief one for the Leopard Gecko. It’s a narrative that encompasses their first brushes with humanity and their ascent to one of the most sought-after reptilian pets.
It’s believed that the initial interactions between humans and Leopard Geckos were dictated by simple curiosity, a mutual fascination of sorts. Early reptile enthusiasts, captivated by the Leopard Gecko’s striking appearance and unique behaviors, began to see the potential in bringing these desert jewels into human habitats. The pet trade took notice, and as knowledge about their relatively straightforward care requirements spread, the domestication wheels were set in motion.
One of the key turning points in the history of leopard geckos as pets was their ability to thrive in captivity. Unlike some other wild species that struggled to adapt, Leopard Geckos showcased a remarkable resilience and flexibility. Their natural behaviors, from nocturnal hunting to mating, were preserved, and with the right care, they even flourished. The evolution in captivity became a testament to their adaptability, turning them into the darlings of the reptile world.
Physical Adaptations of Leopard Geckos
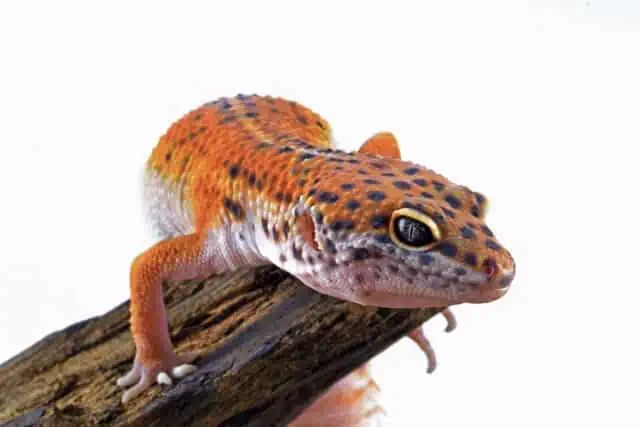

At first glance, the Leopard Gecko captivates with its unique appearance—a mosaic of patterns, intriguing textures, and an unmistakable charm. But delve a little deeper, and you’ll find that each of these physical features isn’t just about aesthetics; they are masterfully crafted adaptations, shaped by eons of evolution. In the wild, every curve, color, and quirk serves a functional purpose, from aiding in camouflage to facilitating hunting. In captivity, these same features play pivotal roles, offering clues to their well-being, moods, and needs.
Unique Skin and Coloring
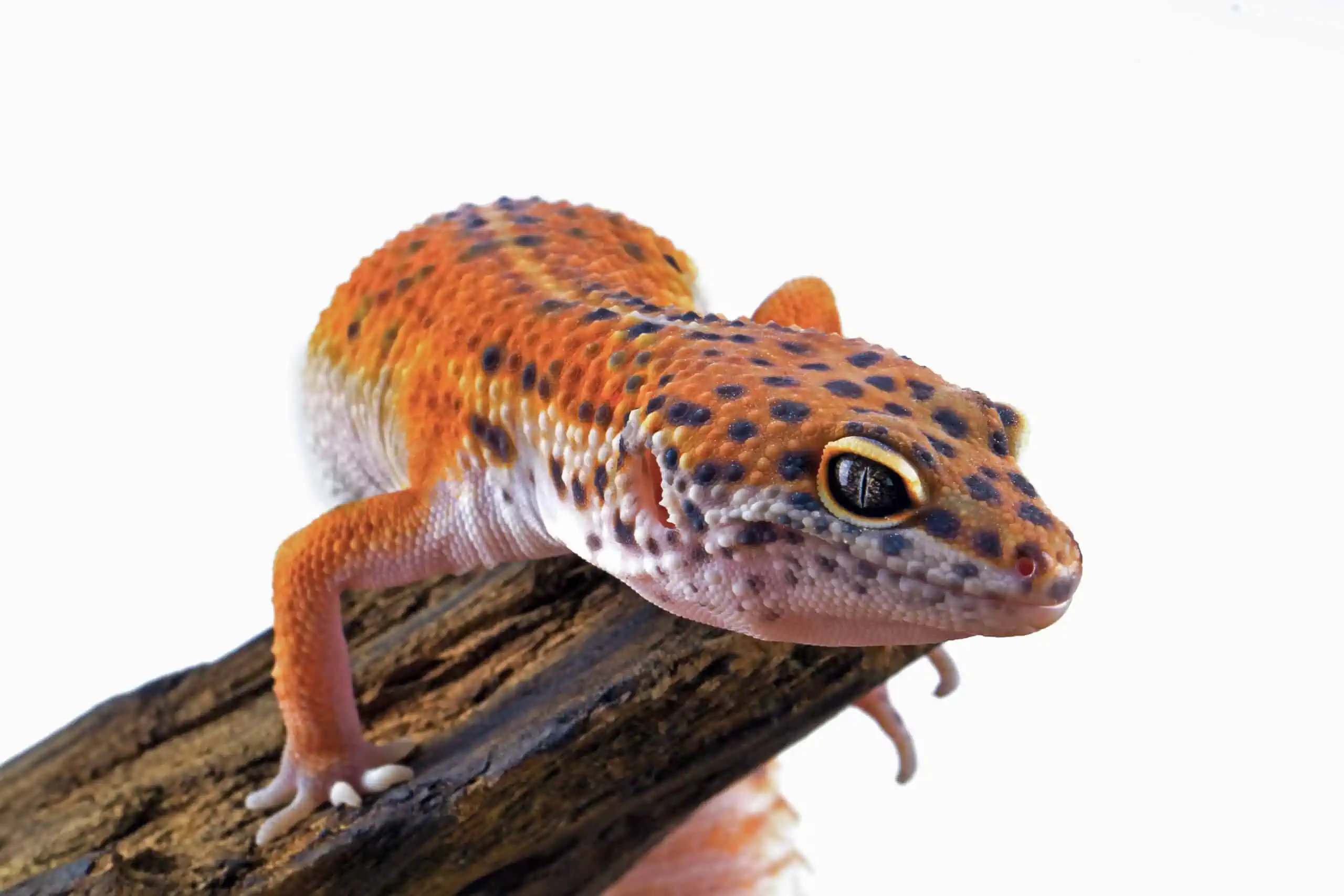
The Leopard Gecko’s skin is truly a marvel of nature, serving as a multifunctional shield and a work of art in one. At the heart of its allure lies the mottled patterns, a blend of spots and stripes, which aren’t just about visual appeal.
First and foremost, these patterns play a critical role in camouflage. The sandy and rocky terrains of their native Asian desert regions are dotted with a mix of shadows, lights, and textures. The leopard gecko patterns allow them to seamlessly blend into this backdrop, offering protection from potential predators. This ability to disappear into their surroundings is vital for their survival, making them less conspicuous to both prey and potential threats.
Beyond its camouflage capabilities, their skin has another essential function: protection. The thick, rough texture, known scientifically as dermal ossifications, provides an added layer of shield against the abrasive desert environment. It prevents dehydration, wards off potential injuries from rough terrains, and even offers a barrier against smaller predatory attempts.
Then comes the fascinating process of shedding. Many often wonder, “Why do leopard geckos shed?” This regular phenomenon is not just about growth; it’s also about rejuvenation. As their outer skin layer gets worn out or damaged, shedding ensures they always have a fresh, healthy layer underneath ready to take its place. For those in captivity, observing the shedding process can provide insights into their health and well-being.
Eyes and Vision
Among the most striking features of the Leopard Gecko are its large, expressive eyes. But these are not merely for show; they’re a testament to the creature’s evolutionary design, catering to its nocturnal lifestyle and challenging habitats.
Leopard Geckos are primarily nocturnal creatures, and their eyes are impeccably designed for night vision. Their large, vertically slit pupils can expand widely in low light, capturing every possible photon to navigate the nighttime landscapes. This adaptation not only aids in hunting under the cover of darkness but also helps avoid daytime predators and the harsh desert sun.
A unique aspect that sets Leopard Geckos apart from many other geckos is the presence of eyelids. Many often wonder, “Why do leopard geckos have eyelids?” Unlike most geckos that have a transparent membrane and clean their eyes using their tongue, Leopard Geckos have movable eyelids. This feature serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it aids in protecting their eyes from the abrasive desert sand. And secondly, these eyelids assist in cleaning and moisturizing the eye surface, ensuring clear vision and eye health.
Another intriguing facet of their vision is the ability to discern a broad spectrum of colors. While it’s not entirely clear how Leopard Geckos perceive colors compared to humans, what’s evident is that their eyesight plays a crucial role in social interactions, recognizing territory, and of course, hunting.
Behavioral Adaptations for Survival
Leopard Geckos, with their lively demeanors and intriguing habits, are more than just a visual delight. Each behavior, each twitch of the tail, and each nocturnal hunt is a window into their evolutionary playbook, designed meticulously over millions of years for survival. As they navigate the challenges of their environment, from finding food to avoiding predators, their behaviors paint a vivid picture of adaptability and instinct. In captivity or the wild, these actions aren’t mere quirks; they’re strategic moves in the grand game of life.
Hunting and Feeding Techniques
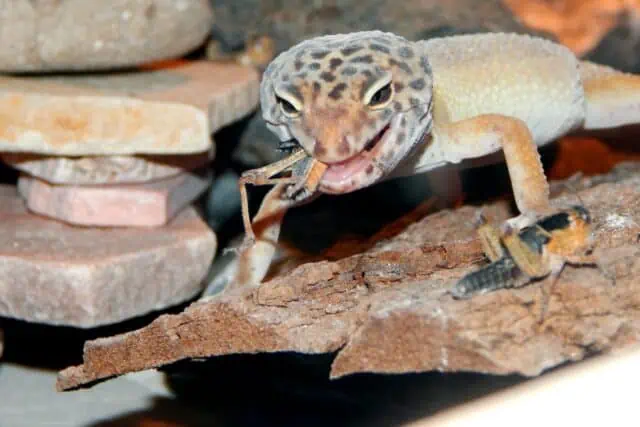
Every twitch, every silent step, every flick of the tongue – when a Leopard Gecko hunts, it’s a dance of precision and patience. Their hunting prowess is not just about satisfying hunger; it’s a choreographed play of instincts and evolutionary tactics fine-tuned over eons.
Leopard Geckos are primarily insectivorous, meaning their diet consists mainly of insects. Crickets and mealworms are among their favorites, both in the wild and in captivity. These insects not only provide the necessary nutrition but also offer a chance for the geckos to engage in their natural hunting behaviors.
So, how do geckos hunt? Their strategy is a blend of stealth and speed. Being nocturnal, they leverage the cover of darkness to approach their prey, often lying in wait or moving slowly to get within striking distance. Once close enough, they pounce with incredible agility, their sharp, snappy jaws ensuring that the prey has little chance of escape.
One might ask, “What else do leopard geckos eat?” In the wild, their diet can be more varied, including other small insects and even occasional spiders. Their preference for hunting at night also gives them an advantage. Many insects are more active during the cooler nighttime hours, making them readily available for a gecko on the prowl.
In captivity, understanding the leopard gecko diet is essential for pet owners. Providing a variety of insects and ensuring they’re gut-loaded (feeding the insects a nutritious diet before offering them to the gecko) helps in mimicking their natural diet, ensuring they receive all the necessary nutrients.
Social and Mating Behaviors
Leopard Geckos, though often seen as solitary creatures, have a rich tapestry of social interactions and mating behaviors. These behaviors, though sometimes subtle, offer a fascinating insight into their world, where every gesture, sound, and movement has meaning.
To start, Leopard Geckos are inherently territorial. This territorial nature isn’t just about physical space; it’s also about establishing dominance and ensuring access to resources, be it food or potential mates. A curled tail, a raised body, or even aggressive posturing are all signals indicating a gecko is marking its territory. In captivity, understanding this can be crucial, especially when considering cohabitating multiple geckos.
When it comes to the intricate dance of mating, Leopard Geckos have their unique rituals and calls. One of the most distinctive aspects is their vocalizations. From chirps to barks, gecko vocalizations play a pivotal role in mating rituals, serving as calls to attract potential partners or even as warnings to rivals.
But it doesn’t stop at vocalizations. Tail vibrations are another intriguing facet of their mating behavior. A vibrating tail, especially from a male, can signal interest or even arousal. Observing such behaviors in captivity can offer keepers insights into their pet’s well-being and even hint at potential breeding readiness.
Answering the question, “How do leopard geckos mate?” takes us further into their behavioral repertoire. Males often approach females cautiously, using a combination of vocalizations, tail movements, and gentle biting. While the process might seem aggressive at times, it’s a delicate balance of assertion and submission, with both parties playing their roles to perfection. If you want to know how to tell males from females apart, we have an article about that.
Adapting in Captivity: Care Guidelines for Owners

The charm of owning a Leopard Gecko isn’t just in their captivating eyes or unique patterns. It’s in the responsibility and privilege of creating a little slice of their natural habitat right in our homes. By understanding their adaptations and needs, owners can ensure a happy, healthy life for their scaly friends. However, there’s a learning curve involved, especially for first-timers. Here, we’ll delve into the intricacies of replicating a natural environment in captivity, highlighting common oversights and offering actionable insights for setting up the perfect terrarium for your Leopard Gecko.
To begin with, setting up a leopard gecko tank isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about functionality that mimics the wild. A proper terrarium setup is paramount. Size matters – ensure that the tank provides ample space for movement, hiding, and hunting. Include natural substrates, climbing structures, and hiding spots. Each of these elements not only adds to the aesthetic appeal but serves practical purposes, from helping with shedding to offering refuge and simulating their natural habitat.
Heating is another crucial element. Leopard Geckos, being ectothermic, rely on external heat sources for thermoregulation. Heating pads placed under one side of the tank can create a temperature gradient, allowing the gecko to choose its comfort spot. Monitoring temperature is crucial; a too hot or too cold environment can lead to health issues.
Humidity levels are just as important. While Leopard Geckos hail from arid regions, they still require a certain level of humidity, especially during shedding. Having a dedicated moist hide with damp moss can aid in this process, ensuring your gecko can shed its skin effectively.
Lighting, contrary to some misconceptions, does play a role in the well-being of Leopard Geckos. While they don’t need specialized UVB lighting like some other reptiles, a regular day-night cycle simulated with lights can be beneficial for their circadian rhythm.
One common mistake new owners often make is overfeeding or offering the wrong diet. As discussed, Leopard Geckos are primarily insectivorous. Providing a varied diet of gut-loaded insects, supplemented occasionally with vitamins and minerals, ensures they get all the nutrients they need.
Lastly, but just as crucial, is regular observation and care. Regularly clean the terrarium, monitor your gecko’s health, and be on the lookout for any behavioral changes. A well-informed owner is a Leopard Gecko’s best ally.
Conclusion
The enchanting world of Leopard Geckos offers a rich tapestry of evolution, adaptation, and survival. Their journey, from the arid landscapes of Asia to the cozy terrariums in our homes, is a testament to their resilience and adaptability. But, as with any living creature, with great wonder comes great responsibility.
Understanding the myriad adaptations of Leopard Geckos isn’t just an academic exercise or a fascinating delve into the natural world. It’s a roadmap for every pet owner, a guide to ensuring the well-being of their scaly companions. Every physical feature, every behavior, every unique quirk carries with it an underlying purpose, honed over eons of evolution. By understanding these, we’re not just appreciating their beauty and complexity; we’re tapping into the essence of what they need to thrive.
For pet owners, the benefits of this understanding are manifold. It leads to better care, a happier gecko, and a more enriching pet ownership experience. Observing a Leopard Gecko in an environment that mirrors its natural habitat, watching it exhibit its natural behaviors, and ensuring its health and happiness is a reward like no other.
FAQs
Why do leopard geckos have tails that detach?
Leopard geckos, like many other lizards, have a defense mechanism known as “autotomy.” This allows them to detach their tails when threatened by predators. The sudden movement of the tail as it detaches can distract predators, giving the gecko a chance to escape. Over time, they can regenerate a new tail, though it might look slightly different from the original.
How often should I feed my leopard gecko?
The feeding frequency for leopard geckos depends on their age. Juveniles should be fed daily since they are growing rapidly, while adults can be fed every other day or even three times a week. It’s essential to ensure a balanced diet, consisting primarily of gut-loaded insects, and to monitor the gecko’s weight and health.
Why does my leopard gecko stare at me?
Leopard geckos are curious creatures. If your gecko is staring at you, it might be trying to figure you out or is simply curious about its surroundings. Sometimes, they also focus on movement or changes in their environment. It’s typically a sign of alertness and interest rather than aggression.
How can I tell if my leopard gecko is stressed?
Signs of stress in leopard geckos can include changes in eating habits, excessive hiding, a lack of activity, aggressive behavior, or rapid breathing. If you’ve recently changed something in their environment or if there’s a lot of noise or activity around their habitat, it could lead to stress. It’s essential to identify the stressor and make the necessary changes to ensure your gecko feels secure.
What should I do if my leopard gecko isn’t eating?
If your leopard gecko isn’t eating, it could be due to various reasons, including stress, illness, or changes in their environment. First, ensure that the terrarium conditions, like temperature and humidity, are optimal. Next, try offering different types of food. If the gecko still doesn’t eat after a few days or shows other signs of illness, it’s best to consult a veterinarian specializing in reptiles.