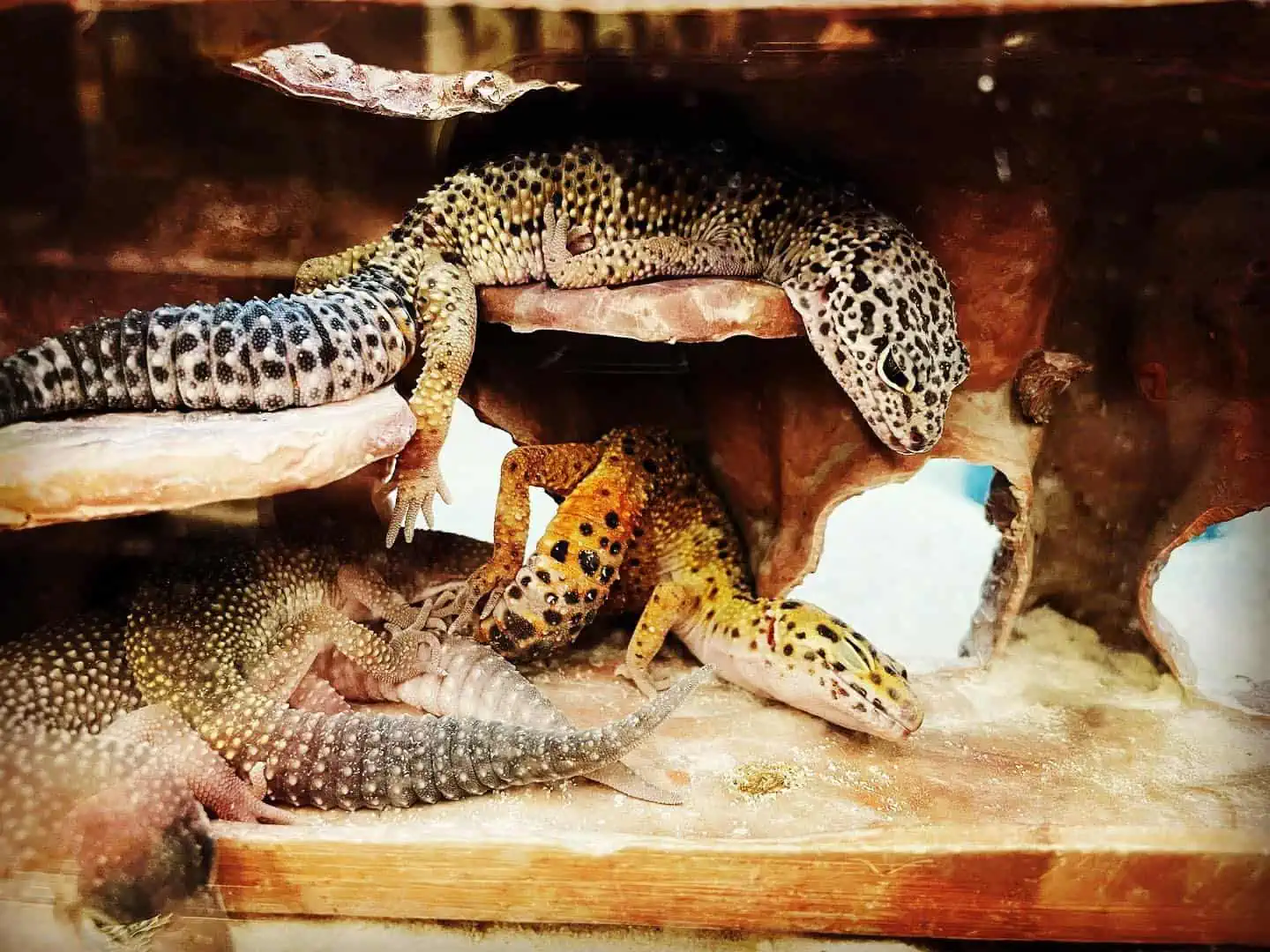
Understanding the sleeping habits of leopard geckos is crucial for anyone owning or looking to own one of these fascinating reptiles. Leopard geckos, scientifically known as Eublepharis macularius, exhibit intriguing sleep behaviors that are vastly different from ours, primarily due to their nocturnal nature.
Nocturnal Nature: Leopard Geckos are primarily nocturnal, with some crepuscular behaviors during twilight hours. This means they are most active at night and during dawn and dusk.
Temperature is Crucial: For optimum health and sleep, leopard geckos require a temperature gradient in their enclosure: a basking area at about 88-92°F (31-33°C), a warm hide around 87-90°F (30-32°C), and a cooler end between 70-78°F (21-26°C).
Lighting Balance: Maintain roughly 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness in their habitat to support their natural sleep cycle and regulate their circadian rhythm.
Provide Hiding Spots: Leopard Geckos need concealed areas to sleep and rest, such as rocky caves or tunnels, mimicking their natural habitat for security.
Potential Sleep Disruptions: Improper diet, lack of vitamin D3, or an inadequate sleeping environment can lead to sleep disturbances and associated health problems, including calcium deficiency.
Are Leopard Geckos Nocturnal Or Diurnal? Their Sleep Behavior Explained
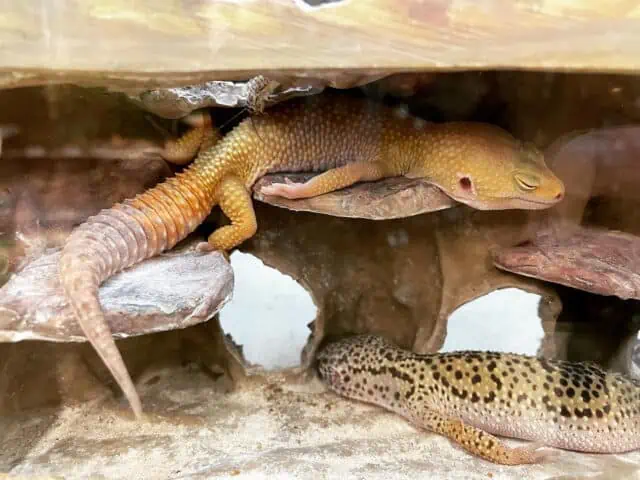

Leopard geckos are renowned for their unique sleep behaviors, characterized by being primarily nocturnal creatures. This nocturnal characteristic implies that leopard geckos are most active during the night, preferring to rest and sleep throughout the day.
It’s a critical adaptation that allows them to avoid the extreme daytime temperatures of their natural environments, typically found in the arid regions of Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iran, and India.
The natural environment of the leopard gecko has played a pivotal role in shaping its sleep patterns. During the day, the high temperatures and predatory birds in their native habitat make it safer and more advantageous to remain hidden and inactive, allowing them to save energy and avoid dehydration.
This behavior has evolved as a survival strategy, enabling them to thrive in harsh desert conditions with scarce food and water.
Several factors contribute to leopard geckos’ preference for nocturnal activity, one of which is their exceptional night vision. This adaptation is enabled by the vertical pupils that allow them to regulate the amount of light entering their eyes, and it facilitates their nighttime hunting of insects and other small prey.
Additionally, their skin coloration, which blends with the natural colors of their environment, aids in camouflage, making it easier for them to avoid predators and hunt more effectively at night.
Creating a suitable sleep environment for leopard geckos in captivity is crucial. It should mimic their natural habitat to support their nocturnal lifestyle, involving appropriate heating, lighting, and hiding spaces to enable restful daytime sleep.
A suitable environment not only supports their sleep behavior but also contributes to their overall health and longevity.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Activity Time | Nocturnal |
| Sleeping Time | Daytime |
| Natural Habitat | Arid regions of Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iran, India |
| Adaptations | Vertical pupils, Camouflaged skin coloration |
| Preferred Environment in Captivity | Mimics natural habitat: appropriate heating, lighting, and hiding spaces |
Sleeping Habits
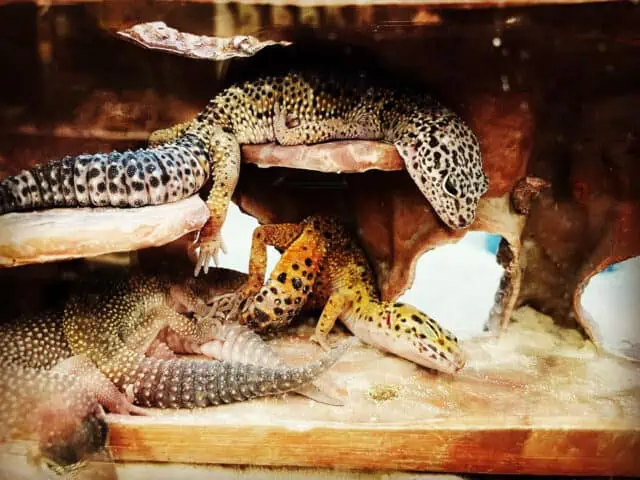

In order to provide the best care for leopard geckos, delving into their sleeping habits is crucial. These nocturnal beings exhibit distinct behaviors and preferences during their active and resting phases, and understanding them is key.
Nocturnal Behaviors
Leopard geckos are fascinating creatures with nocturnal behaviors that are intriguing and complex. They are most active during the night, exhibiting various behaviors that allow them to thrive in their natural habitats. They roam, hunt, and explore, making the nighttime their realm of activity.
One of the most distinctive adaptations of leopard geckos for a nocturnal lifestyle is their vertical pupils. These pupils allow them to see well in low-light conditions, aiding them in their nightly exploits.
Their unique skin coloration is another adaptation that plays a crucial role, enabling them to blend seamlessly into their environment and evade predators. These adaptations are vital as they navigate their surroundings under the cover of darkness, search for food, and avoid danger.
But it’s essential to understand the nuanced distinction between being nocturnal and crepuscular. While nocturnal animals are active at night, crepuscular animals are most active during the twilight hours of dawn and dusk.
Leopard geckos are primarily nocturnal but they also exhibit crepuscular behaviors, showing a burst of activity during the twilight hours. This combination allows them to optimize their time for various activities while staying safe from predators that are active during the day.
Daylight Hours and Sleep Patterns
When the sun is shining and the world is awake, leopard geckos are usually in the midst of their resting phase, retreating to the shadows to sleep. Their sleep patterns are inherently tied to daylight hours, with their natural sleep cycle tuned to the rhythm of the sun.
During the day, they seek refuge in the dark, secluded areas of their habitat, away from the bustling activity and the glaring light.
The amount of light exposure significantly impacts the sleep patterns of leopard geckos. Excessive light can disrupt their natural sleep cycle, causing stress and potentially leading to health issues.
Thus, it is paramount to provide them with a quiet, dark place where they can rest undisturbed during the daylight hours.
Temperature Gradient and Body Temperature Regulation
For leopard geckos, maintaining an optimal body temperature is crucial, and the concept of a temperature gradient within their living space plays a pivotal role in this.
A temperature gradient is essentially a range of temperatures within the terrarium, simulating the varying thermal conditions found in their natural habitat. This gradient allows leopard geckos to regulate their body temperature effectively by moving between different temperature zones, ensuring their metabolic processes operate smoothly.
In order to mimic their natural environment, a leopard gecko’s terrarium should have distinct temperature zones. The basking area should ideally be around 88 to 92 degrees Fahrenheit, while the warm hide, a secluded area where they can retreat, should maintain a temperature of around 87 degrees Fahrenheit.
The cool end of the terrarium should be around 75 degrees Fahrenheit, with nighttime temperatures not dropping below 70 degrees Fahrenheit. These temperature variations provide leopard geckos with options to regulate their body temperature based on their needs at different times.
Social Habits and Sleep Cycles
Leopard geckos exhibit fascinating social habits and sleep cycles that are intricately intertwined with their natural behavior and environmental conditions. Generally preferring a life of nocturnal activity, leopard geckos are most active and lively during the night, a time when they forage, explore, and interact.
Their social interactions and dynamics with other geckos can significantly influence their sleep cycles. Typically, leopard geckos are known to be solitary creatures but can exhibit various social behaviors when housed with other geckos.
The establishment of territories, communal living, and interactions play a role in shaping their daily routines and, consequently, their sleep patterns. It’s crucial to observe the dynamics closely, as tensions between geckos can also affect their sleep.
Creating an Ideal Environment for Sleep
For Leopard Geckos, having an ideal environment is pivotal to ensure they can indulge in their natural behaviors and have proper sleep. A suitable environment, mimicking their natural habitat, not only facilitates their nocturnal activities but also significantly impacts their overall well-being and health.
Warm Hides and Heat Bulbs
Warm hides and heat bulbs are indispensable components in setting up an optimal sleep environment for leopard geckos. These elements replicate the gecko’s natural habitat, providing them with the necessary warmth needed during their resting periods.
Improper heating can cause a range of problems, disturbing the leopard geckos’ sleep patterns and making them uncomfortable, thus forcing them out of their hiding spots.
It’s essential to strike the right balance in terms of heating, ensuring the heat source is adequate, and maintaining appropriate humidity levels within the hiding spots to avoid any discomfort to the gecko. Too much or too little of these can result in stress, making the gecko feel insecure and exposed.
Hours of Light vs. Hours of Darkness
Maintaining a balanced ratio of hours of light and hours of darkness is a fundamental aspect of fostering a healthy sleep cycle for leopard geckos. In their natural habitats, these creatures are accustomed to a fairly even split of daylight and nighttime hours, and mimicking this pattern in their enclosure helps in sustaining their inherent behavior and ensuring their well-being.
Leopard geckos generally thrive when provided with approximately 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. This balance is not merely a reflection of their natural lifestyle, but it is also pivotal in regulating their circadian rhythm, the internal process that dictates the sleep-wake cycle, aligning it with the day-night cycle.
This regulation is crucial as it reinforces healthy sleep patterns, allowing the leopard geckos to remain active and healthy, and enabling them to exhibit natural behaviors.
The Right Balance between Daytime and Nighttime Activities
Finding the correct equilibrium between daytime and nighttime activities is crucial for the well-being of leopard geckos. These creatures exhibit a crepuscular nature, meaning they are most active during the twilight hours of dawn and dusk.
This distinctive behavior affects their activity levels and dictates their overall lifestyle and patterns, making it crucial to adapt their environment accordingly to facilitate their inherent tendencies.
Understanding the nuances between crepuscular and nocturnal behaviors is key in accommodating leopard geckos. Despite their inclination towards twilight hours, they also require a substantial period of darkness at night to rest and sleep, rejuvenating themselves for the following day.
Healthy Sleeping Patterns in Captive Leopard Geckos
Maintaining healthy sleeping patterns is pivotal for the well-being of captive leopard geckos. This involves creating an environment that closely mimics their natural habitat, with provisions for appropriate hiding areas and the correct temperature gradient across their enclosure.
Hiding areas serve as refuge spots for rest, while the temperature gradient allows them to regulate their body temperature effectively, both contributing to healthier sleep cycles.
Ensuring that the leopard geckos’ needs are met in captivity involves more than just their physical environment; their diet also plays a significant role.
Factors such as an improper diet or a lack of essential nutrients like vitamin D3 can disrupt their sleep, leading to stress and potentially causing health issues over time. For instance, a well-balanced diet with the necessary supplements aids in promoting sound sleep and overall health.
Adequate Hiding Spots for the Pet Gecko
It is essential to provide adequate hiding spots for pet geckos, as leopard geckos exhibit a natural preference for resting and sleeping in concealed, secure areas within their enclosure. The provision of such hiding spots allows them to exhibit their natural behavior, ensuring they feel safe, comfortable, and stress-free.
Various hiding options can fulfill this need, such as rocky caves, wood, tunnels, and branches.
The Importance of Sleep for Leopard Geckos
Understanding the significance of sleep is paramount when caring for leopard geckos. Sleep is not just a period of rest for these creatures but a crucial component that affects their overall well-being, health, and behavior.
How Much Sleep do Leopard Geckos Need?
Leopard geckos, as creatures with strong nocturnal tendencies, have unique sleep needs, closely linked to their adaptations and natural behavior in the wild. They primarily sleep during the day, staying hidden in secure, shaded locations and emerging during the twilight hours and at night to hunt and explore.
It’s essential for them to get sufficient rest during the day, usually around 12 hours, to maintain their health and vitality. A balanced sleep cycle allows them to effectively engage in their natural nocturnal activities and crepuscular behaviors.
Potential Health Issues Related to Lack of Sleep
Leopard geckos, when deprived of their much-needed sleep, face various health issues that can be severe and detrimental. A disrupted natural sleep cycle can trigger physiological and behavioral complications, potentially making the gecko vulnerable to calcium deficiency and metabolic bone disease, which are grave conditions requiring immediate attention.
Sleep deprivation can manifest in symptoms such as lethargy, lack of appetite, and irregularities in activity levels, showcasing an immediate need for modifications in their habitat to facilitate proper rest. Furthermore, behaviors such as excessive digging or signs of loneliness (even though they don’t get lonely) can also be indicative of sleep-related problems.