Leopard gecko biting is a behavior often observed when the reptile feels threatened, stressed, or improperly handled. This occurrence can be distressing to both the gecko and the owner, making it crucial to understand why it happens and how to prevent it.
By recognizing the signs of a stressed or nervous leopard gecko, one can effectively reduce instances of biting.
Warning Signs: Observe your leopard gecko for specific signs of nervousness or stress, such as tail waving, rapid breathing, or a defensive posture. These can be early indicators of potential biting behavior.
Gender Differences: Female leopard geckos tend to be less aggressive compared to males. However, during breeding seasons, both genders can exhibit heightened territorial behaviors leading to biting.
Stressful Triggers: Common reasons for biting include inappropriate handling, inadequate enclosure setups (ensure a temperature gradient between 75°F and 90°F), and territorial disputes, especially during mating periods.
Bite Aftercare: Should a bite occur, clean the wound immediately with clean water, apply antibiotic ointment, and monitor for any signs of infection, seeking veterinary care if needed.
Prevention: Consistent, gentle handling and maintaining a stress-free environment, with particular attention to enclosure parameters and gradual introduction of changes, will significantly reduce the chances of biting incidents.
Why Do Leopard Geckos Bite?
Leopard geckos may bite due to a variety of reasons, each pointing back to the reptile’s state of comfort, well-being, and perception of threat. Understanding the motives behind this behavior is integral to fostering a stress-free environment and mitigating any harmful encounters.
Warning Signs of a Nervous or Stressed Leopard Gecko
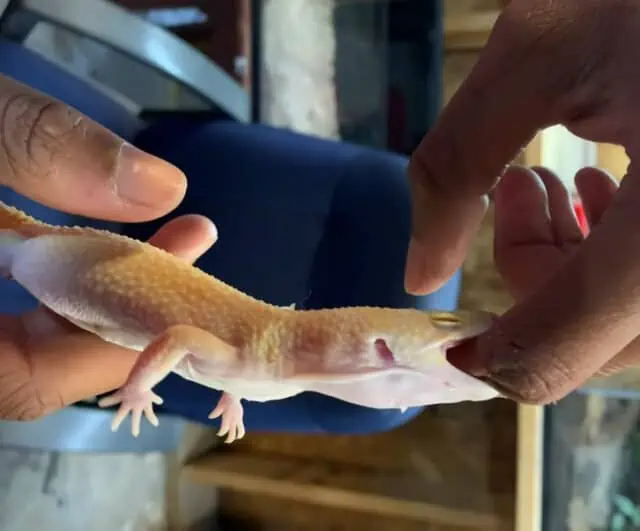

Leopard geckos, like many reptiles, exhibit distinct warning signs when they are nervous or stressed, ranging from making noises to digging. Recognizing these signs early can aid in preventing biting behavior, fostering a safer interaction between you and your gecko.
- Taut Body and Tail: When a leopard gecko is stressed or nervous, its body and tail will often become stiff and taut.
- Rapid Breathing: A noticeable increase in breathing rate can signify distress.
- Vocalization: Leopard geckos may make squeaking or hissing noises when feeling threatened.
- Changing Colors: Some leopard geckos will display darker colors when they are stressed.
- Avoidance or Hiding: Constant avoidance and excessive hiding can be indicative of stress or nervousness.
| Warning Signs | Interpretation | Preventive Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Taut Body and Tail | Stress or Nervousness | Gentle Handling |
| Rapid Breathing | Distress | Calm Environment |
| Vocalization | Feeling Threatened | Safe Enclosure |
| Changing Colors | Stress | Stress-Free Habitat |
| Avoidance or Hiding | Nervousness | Proper Socialization |
Female vs. Male Leopard Geckos Biting
When exploring biting behavior in leopard geckos, it’s important to consider the differences that exist between females and males. Observing and understanding these differences can provide insights into managing and addressing biting behaviors more effectively, ensuring the well-being of both the pet and the owner.
Frequency and Intensity
Male leopard geckos tend to exhibit biting behavior more frequently and with greater intensity than females, often linked to territorial disputes or dominance during the mating season.
Females, on the other hand, might bite primarily due to stress or feeling threatened.
Reasons for Biting
Male leopard geckos often bite due to territorial behaviors or competition with other males, especially in the presence of a female.
Females are generally more passive but may bite if they feel cornered, scared, or are not comfortable with handling.
Approaches to Managing Biting Behavior
For males, providing ample space, minimizing competition, and proper handling can reduce instances of biting.
In females, gentle handling, secure environments, and stress reduction are key to managing biting behaviors.
| Gender | Frequency & Intensity | Common Reasons for Biting | Managing Biting Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male Leopard Geckos | High | Territorial, Competition | Space, Proper Handling |
| Female Leopard Geckos | Lower | Stress, Threat | Gentle Handling, Security |
Common Reasons For Biting
Stressful situations are a predominant factor in causing biting behavior in leopard geckos. By understanding and mitigating these common stressors, the likelihood of biting can be significantly reduced, fostering a more serene environment for your leopard gecko.
Inappropriate Handling: Rough or improper handling can make leopard geckos feel threatened, prompting them to bite in self-defense (you might expect a lick and get a bite, it’s not uncommon when you’re not familiar with geckos). Gentle and confident handling is crucial to build trust and prevent stress.
Inadequate Enclosure Setup: A cramped or improperly set up enclosure can lead to stress. Providing ample space, hiding spots, and a proper temperature gradient is essential for their well-being.
Territorial Behaviors: Leopard geckos are territorial creatures. Placing them in close proximity can lead to aggressive and defensive behaviors, including biting, especially among males.
Environmental Changes: Alterations in their environment, such as new decorations or substrate, can cause stress. Introducing changes gradually can help in acclimation.
Introduction of a New Gecko: The introduction of a new gecko can lead to territorial disputes and stress, increasing the likelihood of biting incidents.
Mating Time: The mating season can heighten territorial and competitive behaviors, particularly in males, making biting more probable.
| Stressful Situations | Impact on Leopard Gecko | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Inappropriate Handling | High Stress, Threat | Gentle, Confident Handling |
| Inadequate Enclosure Setup | Stress, Discomfort | Proper Space, Temperature, Hideouts |
| Territorial Behaviors | Aggression, Defense | Adequate Space, Separation |
| Environmental Changes | Stress, Adaptation | Gradual Changes, Acclimation |
| Introduction of a New Gecko | Territorial Disputes | Proper Introduction, Monitoring |
| Mating Time | Competition, Defense | Monitoring, Separation |
Prevention and Care After a Bite
Navigating through the realms of leopard gecko ownership implies the inevitability of encountering biting behaviors at some point. The emphasis on proactive prevention and diligent aftercare is crucial in maintaining a healthy relationship with your pet while minimizing any adverse effects stemming from a bite.
Preventive Measures: Consistent and gentle handling, stress-free environments, and proper enclosure setups play pivotal roles in bite prevention. Observing your gecko’s behavior and respecting its warning signs can help avoid unnecessary stress and potential biting situations.
Immediate Aftercare: If a bite does occur, it’s imperative to clean the wound immediately with clean water to avoid any infection. Applying antibiotic ointment is also crucial in warding off bacterial infections, promoting quicker healing of the wound.
Monitoring and Veterinary Care: After a bite, monitoring the wound for signs of infection is vital. If any signs of infection are noticed, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, seeking veterinary care is necessary to address any complications promptly.
| Bite Prevention and Care | Importance | Actions and Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Preventive Measures | Avoiding bites, Reducing stress | Gentle handling, Proper environment |
| Immediate Aftercare | Preventing infections, Quick healing | Cleaning, Antibiotic ointment |
| Monitoring and Veterinary Care | Addressing complications | Regular checks, Professional help |